A Rathke’s cleft cyst is a benign growth found on the pituitary gland in the brain, specifically a fluid-filled cyst in the posterior portion of the anterior pituitary gland. It occurs when the Rathke’s pouch does not develop properly, and ranges in size from 2 to 40mm in diameter.
Physiology
The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain.
Rathke’s cleft cyst is a benign growth found on the pituitary gland in the brain, specifically a fluid-filled cyst in the posterior portion of the anterior pituitary gland. It occurs when the Rathke’s pouch does not develop properly, and ranges in size from 2 to 40mm in diameter.
Rathke’s cleft cysts that cause symptoms are relatively uncommon lesions, accounting for less than one percent of all primary masses within the brain. They can occur at any age, although most are identified in adults. Rathke’s cleft cysts sometimes occur together with pituitary adenomas.
Symptoms
Often, Rathke’s cleft cysts do not cause symptoms. Many times, doctors find the cyst while a patient is undergoing a magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI) for a different reason. If the tumor grows to a large size, it may cause symptoms because it is compressing surrounding structures.
Larger Rathke’s cleft cysts may cause:
- Vision loss. This occurs when the cyst grows upward into the brain cavity, compressing the optic chiasm.
- A loss of the outer peripheral vision, called a bitemporal hemianopsia
- When severe, a patient can only see what is directly in front of them.
- Many patients do not become aware of their visual loss until it is quite severe.
- Other visual problems can include:
- Loss of visual acuity (blurry vision), especially if the cyst grows forward and compresses an optic nerve
- Colors not perceived as bright as usual
Diagnosis
Diagnostic procedures include:
- MRI
- Hormone testing
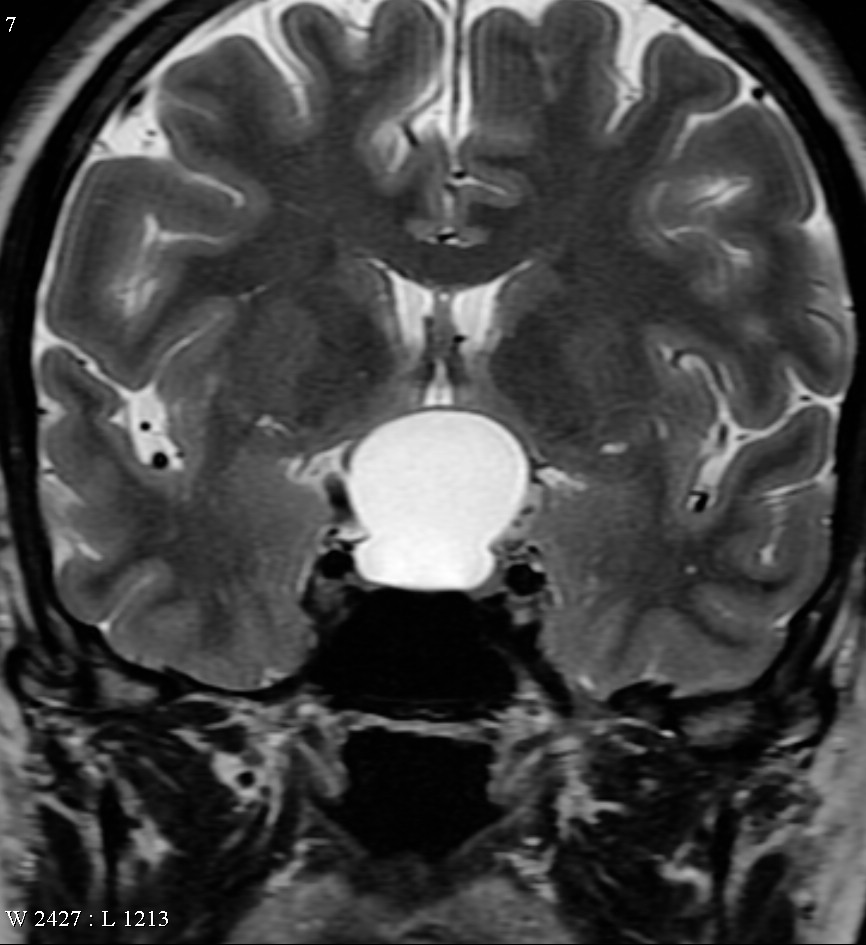
MRI Imaging
MRI of the pituitary gland can visualize the tumor.
In order to confirm a diagnosis of Rathke’s cleft cyst, your doctor you need to rule out other possible conditions that present with a pituitary cyst:
- An arachnoid cyst
- Cystic pituitary adenoma
- Craniopharyngioma
Hormone Testing for Rathke’s Cleft Cyst
If your symptoms suggest pituitary failure (hypopituitarism), a complete evaluation of the endocrine system has to be done. Based on results of these blood tests, additional hormonal studies may be requested.
Surgery for Rathke’s Cleft Cyst
Surgery for Rathke’s cleft cysts includes draining the fluid from the cyst.
- The removal of the cyst wall, may turns into pituitary insufficiency. Often, diabetes insipidus develops.
- “Marsupialization” of the cyst, which means making a large opening at the bottom of the cyst, may prevent cyst recurrence in some cases.
Minimally invasive endoscopic technique is often used. The endoscopic approach can minimize complications, hospitalization time and discomfort
This advanced technique requires specialized training and equipment and should be performed at a dedicated pituitary tumor center.
 English
English Italiano
Italiano